Friday, April 18, 2014
Tuesday, April 1, 2014
Thursday, March 20, 2014
Linear Programming
Vertices:
|
||||||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C=3x + 4y
|
|||||||
x ≥
0
y ≥
0
x + y ≤ 6
|
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
Vertices:
|
||||||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C=2x + 5y
|
|||||||
x ≤ 5
y ≥ 4
-2x + 5y ≤ 30
|
10
|
50
|
30
|
|||||
|
|
||||||||
Vertices:
|
(1,8)
|
(1,2)
|
(5,2)
|
|||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C=7x + 3y
|
|||||||
x ≥ 1
y ≥ 2
6x + 4y ≤ 38
|
31
|
11
|
41
|
|||||
Vertices:
|
(0,4)
|
(0,8)
|
(6,8)
|
|||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C=4x + 6y
|
|||||||
x ≥
0
y ≤ 8
-2x+3y ≥ 12
|
28
|
52
|
240
|
|||||
Vertices:
|
(0,0)
|
(0,5)
|
(2,3)
|
(8,0)
|
||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C=8x + 7y
|
|||||||
x ≥
0
y ≥
0
4x + 4y ≤ 20
x + 2y ≤ 8 |
15
|
64
|
35
|
37
|
||||
Vertices:
|
(3,0)
|
|||||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C=3x + 5y
|
|||||||
x ≥
0
2x + 3y ≥
0
x + y ≤ 5
|
C=27
|
C=20
|
C=10
|
|||||
Monday, March 10, 2014
Friday, February 28, 2014
Graphing Exponential Growth & Decay
Graphing Exponential Growth & Decay
Y- a×b x-h +K
A- Multiplier
A>1- Stretch
A<a<1- Compression
A<0 (negative)- Flipped over x-axis
B- Base has an exponential (always positive)
0>b<1- Decay (always decreasing)
Asymptote-y=k
Domain-(-∞, ∞) =all real numbers
Range-y>k (a=positive)
y<k (a=negative)
Exponential equations domain is always all real numbers.
Thursday, February 27, 2014
General Forms of a Sequence
General Forms of a Sequence
Arithmetic Sequence- the difference between one term and the next is a constant. Also called the Common Difference.
Geometric sequence formula- In a Geometric Sequence each term is found by multiplying the previous term by a constant. Also called the Common Ratio.
Finite sequence- Is a function with domain 1,2,3.
Infinite sequence- Is a function with domain 1,2,3,4.... etc.
Series- Is the sum of a sequence.
Explicit formula- Each domain is an answer not based on any values.
Recursive Formula- Each domain is a answer based on a previous answer.
Tuesday, February 25, 2014
Compound Interest Formula
Compound Interest Formula
P= principal amount (the initial amount you borrow or deposit)
r= annual rate of interest (as a decimal)
n= number of years the amount is deposited or borrowed for
A= amount of money accumulated after n years, including interest
n= number of times the interest is compounded per year
Example: An amount of $1,500.00 is deposited in a bank paying an annual interest rate of 4.3%, compounded quarterly. What is the balance after 6 years?
Solution: Using the compound interest formula, we have that
P = 1500, r = 4.3/100 = 0.043, n = 4, t = 6.
So,the balance after 6 years is approximately $1,938.84.
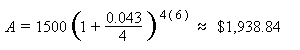
Wednesday, January 15, 2014
Characteristics & Traits of Graphing
Characteristics & Traits
- Domain: x-values, describe a graph as it moves left to right.
- Range: y-values, describe a graph as it goes up and down.
- End Behavior: describes what happens an both ends.
- Absolute Max/Min: Highest or lowest point.
- Local Max/Min: More than one highest or lowest point.
- Interval of increase: What happens to the graph as you move along the x-axis.
- Interval of decrease: What happens to the graph as you move along the x-axis.
- X-intercept: (a,0)
- Y-intercept: (0,b)
- Symmetry:
Even: Symmetric about the y-axis.
Odd: Symmetric about the origin.
Neither: No symmetry
- Asymptotes: Imaginary line that a graph gets closer to, but never touches.
- Function: Passes vertical line test.
- One to One: Passes both line tests.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)











.jpg)
